Has Esports Helped the Game Industry?
Is it a competitive market?

Esports has come a long way: from high-score chasing, to the Battle By the Bay, the World Cyber Games, and much more. It wasn’t until the 2010s that the legitimacy and ubiquity of esports reached a fevered pitch, with studios chasing after this market and the push to give esports as big of a profile as traditional sports. But as I looked at genres like fighting and RTS, I started to think about whether esports has helped or hurt game development.
The Intended Effect
Esports and live service have gone together since the 2000s and the rise of League of Legends. The idea was that by creating an esport, a game would become popular outside of just playing the game; people would follow the esport and sponsors could sell ad revenue. There has always been this dream in the US to have esports reach the same level of recognition and impact that we saw in South Korea with StarCraft.
By continuing to support a game with more content, it would mean people would spend money on said content, and more support would keep a game going for years. When you look at the big successes — LoL, CS: GO, Rainbow Six: Siege, and so on – it does turn into that. For multiplayer, it has been a godsend in terms of keeping these games relevant and playable for years thanks to people continuing to play for the competitive side. This symbiotic relationship has been the envy of publishers and developers who all tried to make their own take on these games, as we saw with the numerous battle royales, MOBAs, shooters, and so on. And while esports has been good to these games it hasn’t been good to the health of these genres.
The problem is that making an esport and making a marketable game might not be as compatible as you think.
Making an Esport
Esport design is different from the traditional design and mechanics we see in other games. When you are building an esport, you must focus on the competitive side — all map design, all balancing, all future content, must be built around what the competitive people want to see. This has been the driving factor for fighting games for years and was part of what led to the decline of traditional RTS games in the mainstream in favor of MOBAs.
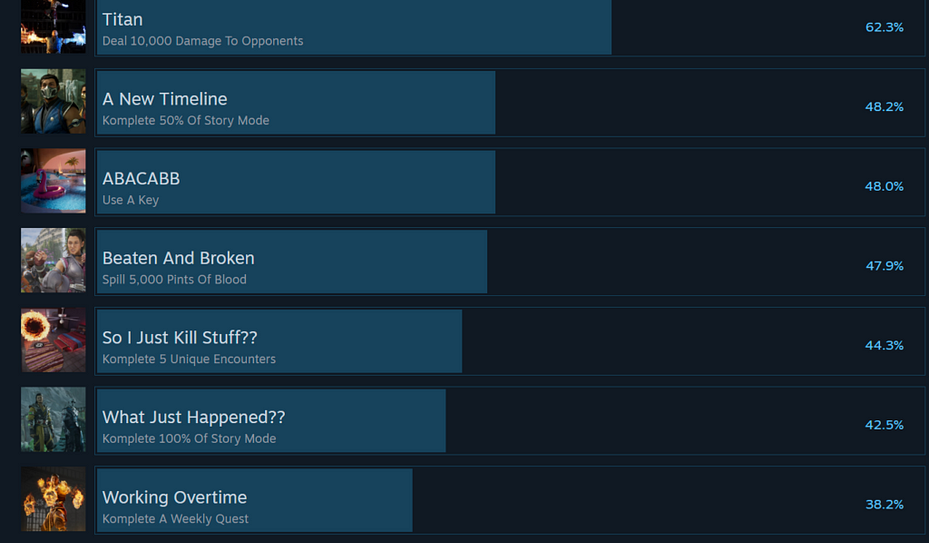
An esport is all about “the match” and everything that isn’t related to it is seen as fluff to the competitive side.
Matches are meant to be as balanced as possible and favor player skill above all else. With every esport game mentioned in this piece, you’ll find very little content outside of that. For the games that do add in single-player or story content, with rare exceptions (that I’ll come back to below), it is kept minimal and seems like something added to check off a list.
Casual vs. Competitive
When we look at games and genres that have gone out of their way to be the next esport, it’s time to face an important truth: esports suck the fun out of those games. From a community standpoint, some of the worst games imaginable, with regard to community management and moderation, are from the esports side. You have those who send horrible messages to other players, players who look down on everyone else, and reports of corruption and cheating from time to time.
From an onboarding and UI/UX point of view, these games are ineffective at providing accommodations and educating new players on how to play competitively. When it comes to the importance of UI/UX design, esports games fail this test time after time, and a lot of it comes down to their player base, specifically the esports side. Just as single-player gamers often fail to understand the difference between complexity and depth, so do a lot of multiplayer fans. Some immediately fume the second someone wants to change a game to make it easier to play or modernize it for audiences today, as we saw with the modern controls debate from Street Fighter 6. The problem is that teaching someone how to play against an AI is not the same as teaching them how to fight another player. For games that introduce new rules and mechanics, onboarding and tutorials may never cover those advanced elements.
In the last section I mentioned that esports players tend to focus on match design and match balancing above all else, however, the “else” in this regard is what attracts people to play these games in the first place. An esports player wants something that is consistent across however many matches they tend to play over the game’s lifespan and this is also why progression, outside elements, or those that don’t fit within the match are viewed as negatives. For everyone else, this kind of stuff is what makes these games appealing. Something I wrote about in my RTS book with unit design is that at the end of the day, cool trumps balance. Are the different factions in the Command & Conquer universe or the races in StarCraft 2 perfectly balanced? Heck no, and any self-respecting fan would say the same.

Keeping with StarCraft 2, it's the only game I can think of that came out with a fully supported esports model with its competitive play and a completely original campaign for each faction featuring unique units and progression not seen anywhere else. This is in line with how NetherRealm Studios revitalized the fighting game genre in the late 2000s by focusing on content for people who have no interest in the competitive side.
Esports players, no matter how much money gets thrown at sponsorships and tournaments, represent a fraction, of a fraction, of a fraction, of your consumer base, and it's why only catering to them does not keep a game financially afloat.
Where the Money Comes and Goes
Live service game design is all about money coming in and going out in a continuous cycle. If you’re not creating new content, money stops coming in, which means no more budget to create new content. And if you’re not creating “attractive” content for people to buy, then you are just wasting development time and money.
The issue with catering only to esports players with your game’s content and growth is that it doesn’t leave room for anyone else to keep playing. You’ll see this with any competitively-driven game — the first month or two will have peak player counts with new players trying to learn the game and see if it works for them. And then, without fail, those numbers plummet and the people who stick around are just the competitive side or those trying to be competitive.
Source: Author.
This group only cares about one thing: content that plays into the competitive side of the game. Anything else is not of interest to them, and if you think new cosmetics are going to be enough to bring casual players back, that’s not going to work. To that point, trying to create new game modes, new mechanics, or anything that runs counter to the esports/competitive side will be met with angry esports players, and still may not be enough to get people to come back. Blizzard’s strategy of splitting StarCraft 2 down the middle between the competitive and casual sides with its content was a brilliant move. Conversely, trying to shoehorn competitive and casual together is what doomed Command & Conquer 4.
The problem with trying to cater to an esports market is that instead of being able to grow your game with new content and interest over the months and years, it starts to shrink. Once a game’s audience becomes fixed like this, no one new is going to join, and if they do, chances are they won’t stay long. If players feel like they are just there to be served up to the expert players, they will leave even faster, as Activision’s report on Skill-Based Matchmaking covers in detail.
The Better Live Service
Some of the most popular live service games today come from the mobile space and are as far away from competitive experiences as a game could get. Creating attractive content for a live service game requires making sure that all segments of your audience can experience it. If there are new missions, storylines, etc., then they should be accessible to all groups. For bonus challenges or limited-time events, there needs to be content for each group of players.
Whenever there is content that only one group of players can use or will support, it’s going to push the other ones away; you need as wide of a consumer base as possible if you want your game to keep growing.
What Is the Future of Esports?
Esports is in a very awkward place now; it’s no longer the new thing on the market, and tournaments like the LoL Championship Series and EVO have reached the mainstream, but prospects for continued growth are debatable. Part of the problem is that it’s not about organically making a game an esport, where the process would look like this:
- The game comes out
- People like to play it
- Tournaments are developed
- The game becomes an esport
Now, many developers and publishers are chasing the market to will their games to become an esport. The ones that specifically are built for esport players are not finding a market outside of just those players.
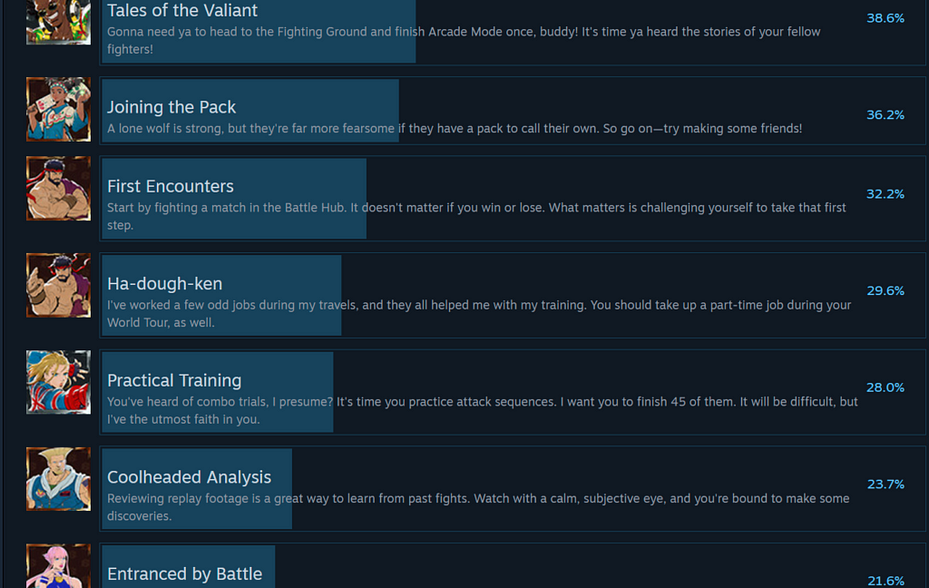
Just as the RTS genre needs to have a hard talk about modernizing and appealing to more people, the fighting genre needs a similar one.
Despite how many copies Street Fighter 6 sold and how popular it was, less than half the player base on PC tried a multiplayer match. Designing additional content for mainstream and non-competitive players has helped, but it doesn’t fix the inherent problem of trying to get someone who isn’t a pro player interested in playing a game designed around that mindset.
What do you think: Is esports going to keep growing, or has it reached its limits?
